Zephyr® Valves: Most Studied. Most Proven. Most Used Valves for Severe COPD/Emphysema.*
The Zephyr Valve is a clinically-proven bronchoscopic treatment for patients with severe COPD/emphysema who suffer from dypsnea despite optimized medical therapy.
The 2024 GOLD Report summarized the following patient benefits reported in clinical studies on Endobronchial Valve (EBV) Treatment for severe COPD/emphysema:42
- Improved FEV1, 6MWD, and health status at 6 and 12 months**
- Improved survival after successful treatment (4 retrospective studies)
- Decreased exacerbations
- Decreased respiratory failure episodes

Complications of the Zephyr Valve treatment can include, but are not limited to, pneumothorax, worsening of COPD symptoms, hemoptysis, pneumonia, dyspnea and, in rare cases, death.
*Data on file at Pulmonx
**Quality and quantity of data was rated “Evidence Level A.”
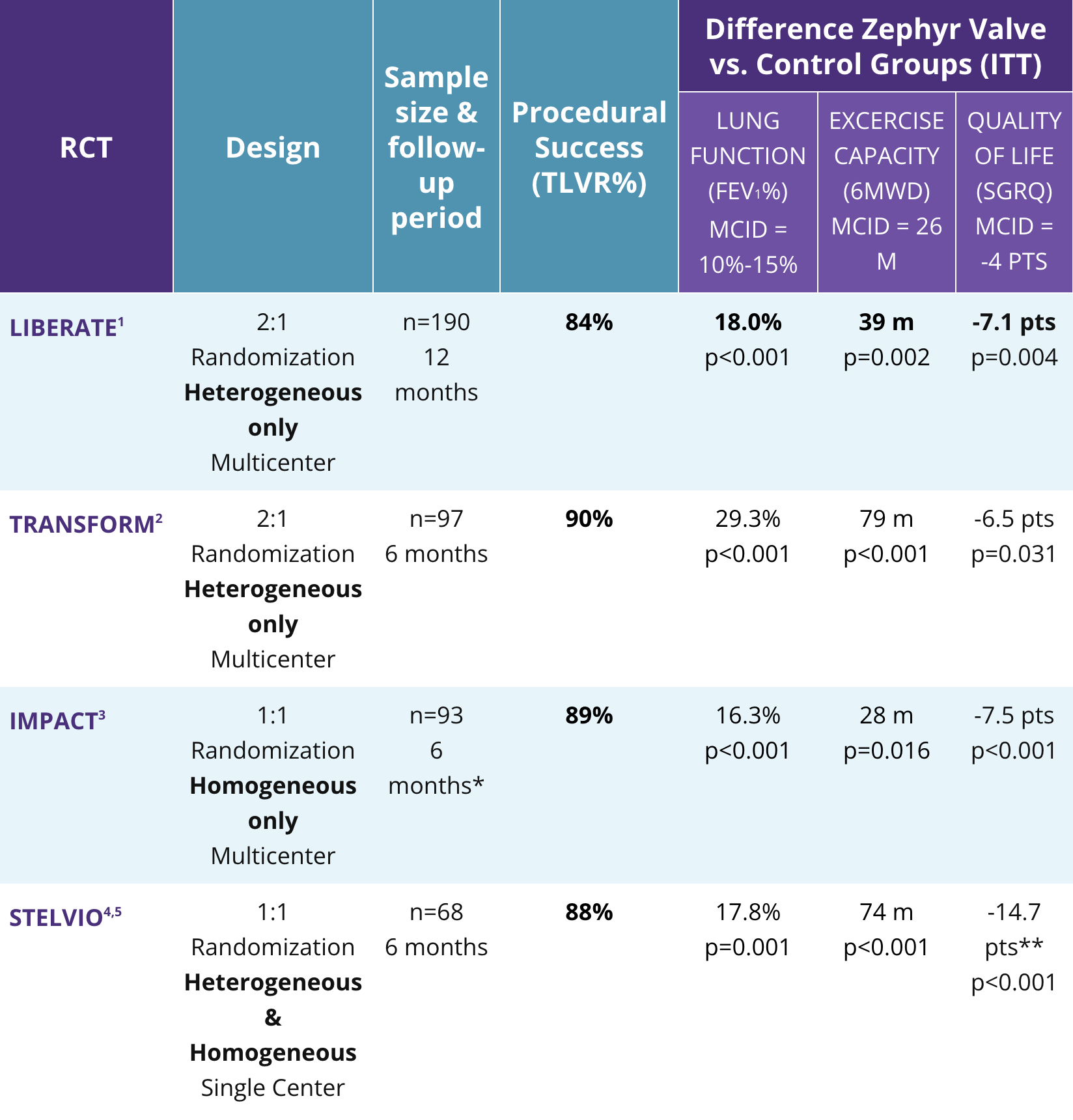
Consistent Clinical Findings
Across Four Randomized Controlled Trials
Completed cases, all other values listed are ITT population
*Data on file at Pulmonx (not in publication)
**Completed cases, all other values listed are ITT population
Recent Clinical Data
Download Clinical Study Summaries
Click the logo to download the summary
International Guidance Documents Include Endobronchial Valve Treatment as an Option for Emphysema Patients
Multiple independent networks have concluded that with proper patient selection, endobronchial valves, such as Zephyr Valves, should be considered in the treatment of severe emphysema.
The quality of evidence for treatment with endobronchial valves has been graded “A” by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD).10
The United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has included this treatment as part of standard measures for COPD and recommended all qualifying patients be evaluated for eligibility.11,34