Zephyr® Valve: Treatment for Severe COPD/Emphysema
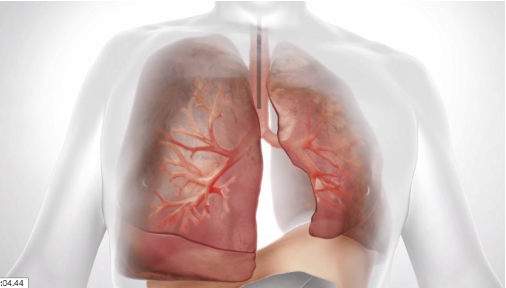
Reducing Hyperinflation, an Underlying Cause of Breathlessness
The majority of patients with advanced COPD/emphysema are treated with inhalers, medications and pulmonary rehabilitation. However, none of these treatments address the root cause of dyspnea – hyperinflation of the lungs. Thus, many patients – even stable patients – still experience significant breathlessness. And this, in turn, can result in the downward cycle of less activity, compromised quality of life, and increased dyspnea.
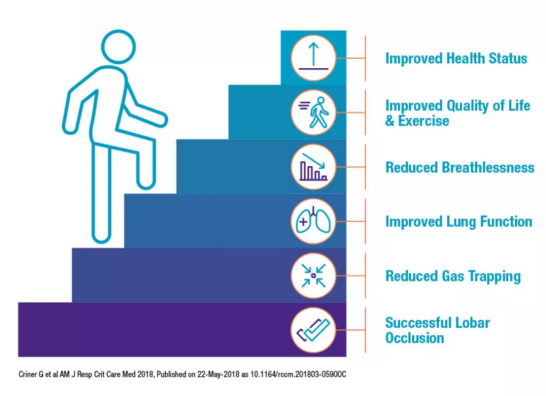
Zephyr Valve treatment leads to improved health status. Patients treated with Zephyr Valves experienced clinical benefits and improved quality of life when compared to patients who were on medications alone.1
Zephyr Valve Treatment1
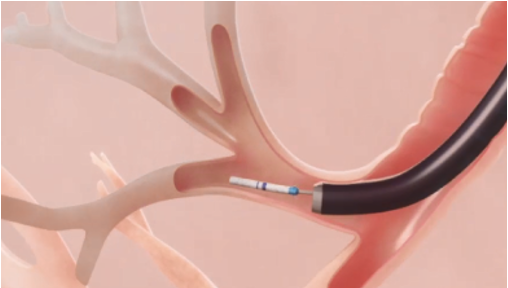
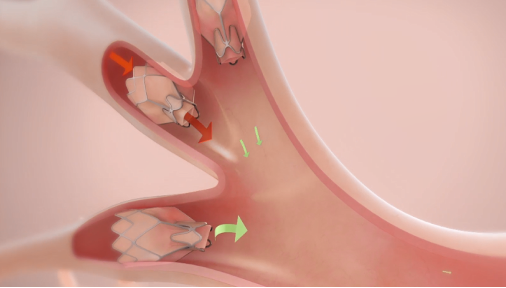
How Zephyr Valves Work
Minimally Invasive Bronchoscopic Procedure
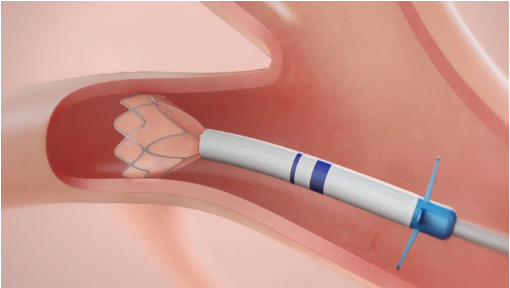
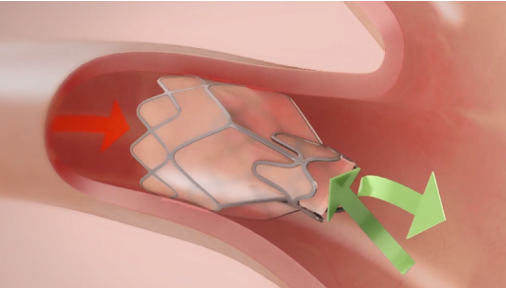
Zephyr Valves are placed via a bronchoscopic procedure which is usually conducted under general anesthesia. The one‑way Zephyr Valves are placed into all of the airways that feed the targeted lobe. This allows the lobe to deflate during exhalation, but prevents new air from entering during inhalation. This results in atelectasis of the treated lobe and reduced lung volume.
The procedure typically takes approximately one hour.
This mechanical solution alleviates shortness of breath by targeting the root cause – hyperinflation – and can provide a greater benefit than medications alone.1
Complications of the Zephyr Valve treatment can include, but are not limited to, pneumothorax, worsening of COPD symptoms, hemoptysis, pneumonia, dyspnea and, in rare cases, death.
Zephyr Valve Procedure Overview
Pulmonologist Perspective: How Zephyr Valves Work
Watch Zephyr Valve physicians discuss the procedure and the benefits patients may experience in their overall quality of life.
Physicians are paid consultants of Pulmonx Corporation.
Post-Procedure Management
After the procedure, the patient will stay at least 3 nights in the hospital under observation. This is important to monitor if the patient is experiencing any side effects post-procedure. The major significant side effect associated with the Zephyr Valve procedure in the short-term is pneumothorax.
Targeted lobar deflation can cause inflation of the ipsilateral lobe, which can result in a tear of the already compromised parenchymal tissue of the emphysematous ipsilateral lobe, resulting in a pneumothorax.
In the LIBERATE Clinical Study, subjects experiencing a pneumothorax attained the same level of benefit over the long-term as those without pneumothorax.1
Patients should also be monitored for pneumonia, COPD exacerbations, and respiratory failure, as these events have been observed in patients treated with Zephyr Valves.