Patient Selection for the Zephyr® Valve
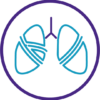
The Zephyr Valve is a clinically-proven bronchoscopic treatment for patients with severe COPD/emphysema who suffer from shortness of breath despite optimized medical therapy.
Appropriate patient selection is critical to the success of Zephyr Valve treatment. Over time, clinical trial data have helped define the successful patient profile.1-4,6,7 The Zephyr Valve is the first endobronchial valve to receive approval from the FDA for patients with either heterogeneous or homogeneous emphysema and can be used to treat the upper and lower lobes of either lung.
Patient Eligibility for Zephyr Valve Treatment
If shortness of breath is not controlled with medical management, patients may qualify for Zephyr Valve Treatment.
Medical History
- Full medical treatment for COPD
- With or without supplemental oxygen
- Stable or unstable
- Persistent COPD symptoms
Clinical Presentation
- Severe COPD/emphysema
- Shortness of breath upon activity or rest
- Limited in daily functions
- Dissatisfied with activity level and quality of life
Diagnostic Checklist for Zephyr Valve Treatment Eligibility
Zephyr Valves have been clinically proven in:
- Heterogeneous and homogeneous emphysema
- Upper lobe and lower lobe predominant emphysema
Diagnosis and Symptoms
![]()
Severe COPD/emphysema
![]()
Shortness of breath upon activity or rest
Evidence of Obstruction
![]()
Spirometry: FEV1 < 50% predicted, post-bronchodilator
Evidence of Hyperinflation
- Body Plethysmography: RV >150% predicted
Nitrogen Washout Lung Volumes are not recommended* - Imaging: Chest X-ray: Flattened diaphragm
- HRCT: Evidence of emphysematous tissue
6 Minute Walk Test
![]() 100 to 500m / 328 to 1640 ft
100 to 500m / 328 to 1640 ft
Smoking Status
![]() Non-smoking or willing to quit smoking
Non-smoking or willing to quit smoking
*Gas dilution PFT tests, like Nitrogen Washout or Helium Dilution, have been shown to underestimate TLC & RV because only communicating gas volume is measured in these tests. In the presence of severe airflow obstruction, TLC can be underestimated by a gas dilution method by as much as 3 liters.
Contradictions42
- Patients for whom bronchoscopic procedures are contraindicated
- Patients with evidence of active pulmonary infection
- Patients with known allergies to Nitinol, Nickel, Titanium, or Silicone
- Patients who have not quit smoking
- Patients with large bullae encompassing greater than 30% of either lung
Warnings42
- Prior lung transplant, LVRS, median sternotomy, or lobectomy
- Congestive heart failure (left ventricular ejection fraction <45%); myocardial infarction
- FEV1 < 15% of predicted value
Identifying Patients for Zephyr Valves
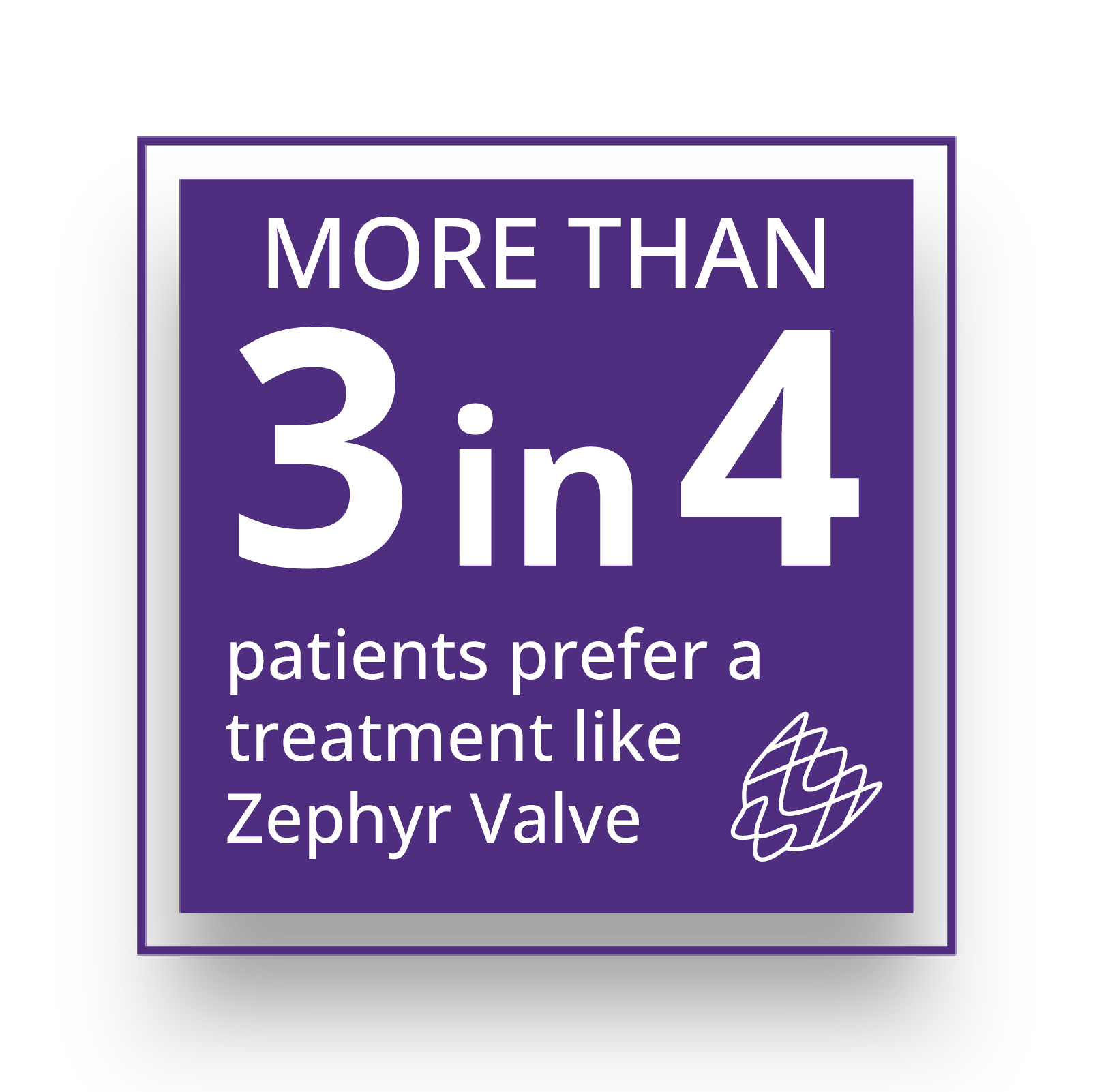
“Thinking about endobronchial valves is part of the checklist that I go through for every single patient that I see.”
Dr. MeiLan Han, Chief of Pulmonology and Critical Care, University of Michigan Health
The Treatment Process
Step 1:
- Full Pulmonary Function Testing using Body Plethysmography
- 6 Minute Walk Test
- High Resolution CT Scan with specialized protocols
- Echocardiogram
- Arterial Blood Gas (optional)
- Perfusion Testing (optional)
Step 2:
- StratX Report to support lobe selection:
- Lobar volume
- Emphysema destruction score
- Fissure completeness
Step 3:
- Chartis System
procedure - Confirm target lobe has no collateral ventilation
Step 4:
- Zephyr Valves placed to completely occlude the target lobe
Step 5:
- Patient should remain in the hospital for a minimum of 3 nights following the procedure for observation