
Benefits are in line with those seen with LVRS (lung volume reduction surgery), and the consistent trial results, potential reduction in post-procedure morbidity, and reversibility of the procedure position Zephyr treatment as a viable treatment option in those who remain symptomatic on maximal medical therapy.”2
Published in The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine2
A multicentre, multinational randomised controlled trial of Zephyr® Endobronchial Valves in patients with heterogenous emphysema and little to no collateral ventilation
Methods & Endpoints
-
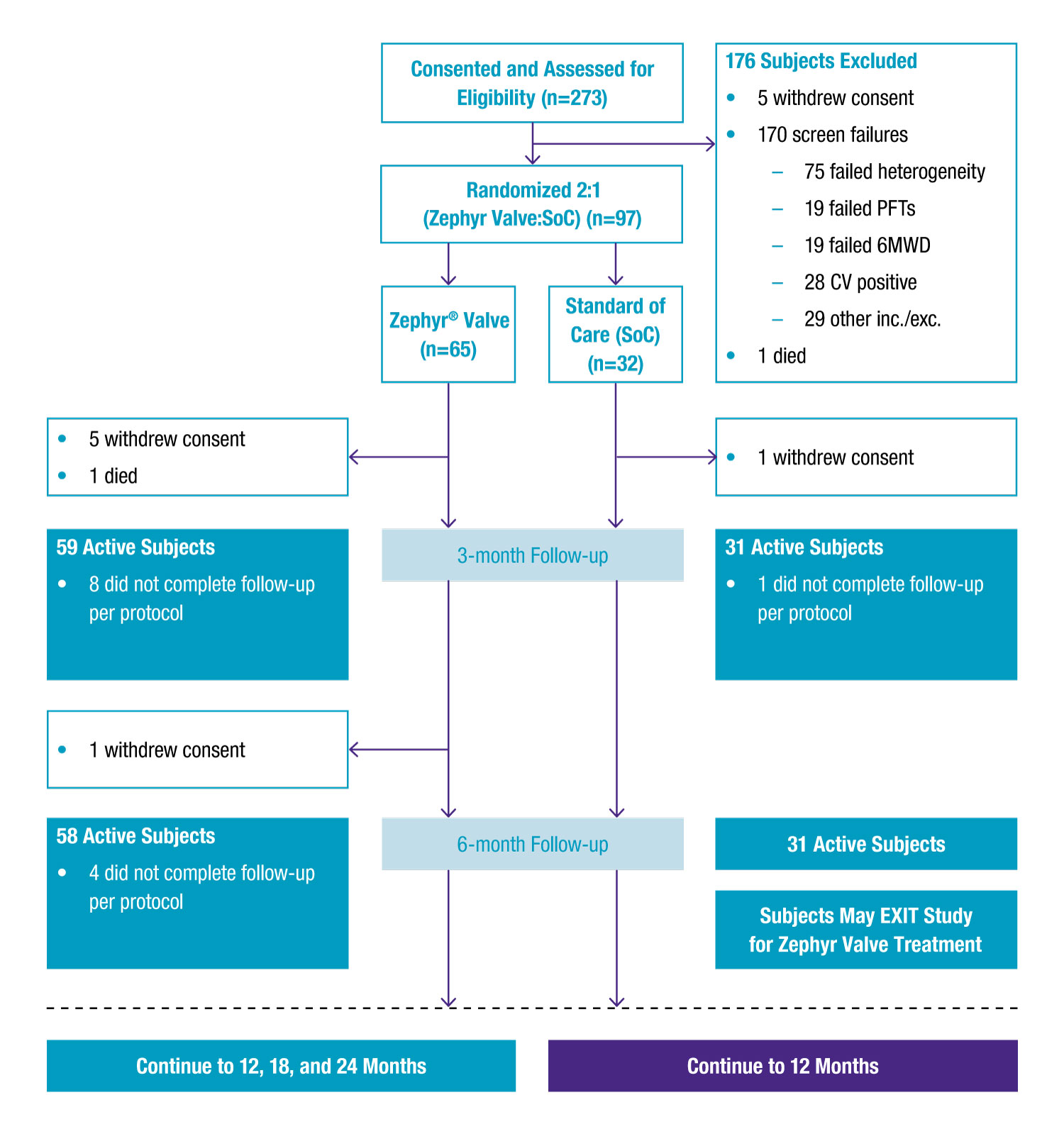
97 patients with heterogeneous emphysema were confirmed with the Chartis® System to be collateral ventilation (CV) negative and likely responders to Zephyr Valve treatment, and randomised 2:1 to either Zephyr Valve treatment or medical management.
-
For Zephyr Valve-treated patients, target lobes were selected based on emphysema destruction scores and regional perfusion impairments and were then completely occluded with valves.
-
Valve position was assessed at 45 days post-implant by CT and removed and replaced, if necessary.
Study Design
Reasons for Withdrawn Consents
- 5 Zephyr Valve subjects before 3-month visit: 1 difficult anatomy for Zephyr Valve placement; 1 experienced two pneumothoraces and worsening COPD; 2 for lack of perceived benefit; 1 non-compliant, withdrawn by investigator
- 1 Zephyr Valve subject between 3- and 6-month visit: Worsening COPD, all valves removed, subject withdrew consent
- 1 SoC subject before 3-month visit: Exited study to pursue Zephyr Valve treatment outside of the study
Results
Primary Endpoint
Percent of subjects achieving a 12% or greater improvement in FEV1 (L)
Secondary Endpoints in the Intent-to-Treat Population
Figure 2a: FEV1 Improvement
TRANSFORM - FEV1 - Line | amCharts
Figure 2b: 6MWD Improvement
TRANSFORM - 6MWD - Line | amCharts
Figure 2c: RV Improvement
TRANSFORM - RV - Line | amCharts
Figure 2d: SGRQ Improvement
TRANSFORM - SGRQ - Line | amCharts
Figure 2e: BODE Index Improvement
TRANSFORM - BODE - Line | amCharts
3 Months
Zephyr Valve n=65, SoC n=32
6 Months
Zephyr Valve n=65, SoC n=32
Legend to Figure 2: Data presented are mean ± SEM for changes from baseline to 3 and 6 months post bronchoscopy for Zephyr Valve, SoC, and difference between Zephyr Valve and SoC. Figure 2a: FEV1 (L); Figure 2b: 6-Minute Walk Distance (m); Figure 2c: RV (L); Figure 2d: St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; and Figure 2e: BODE Index.
Conclusion
Zephyr® Valve treatment results in clinically meaningful and statistically significant benefits in lung function, dyspnea, exercise tolerance, and quality of life over current standard of care medical therapy when used in hyperinflated subjects with heterogeneous emphysema without collateral ventilation in the target lobe.
Complications of the Zephyr Endobronchial Valve treatment can include but are not limited to pneumothorax, worsening of COPD symptoms, hemoptysis, pneumonia, dyspnea and, in rare cases, death.



